OLEFIN

Plant:
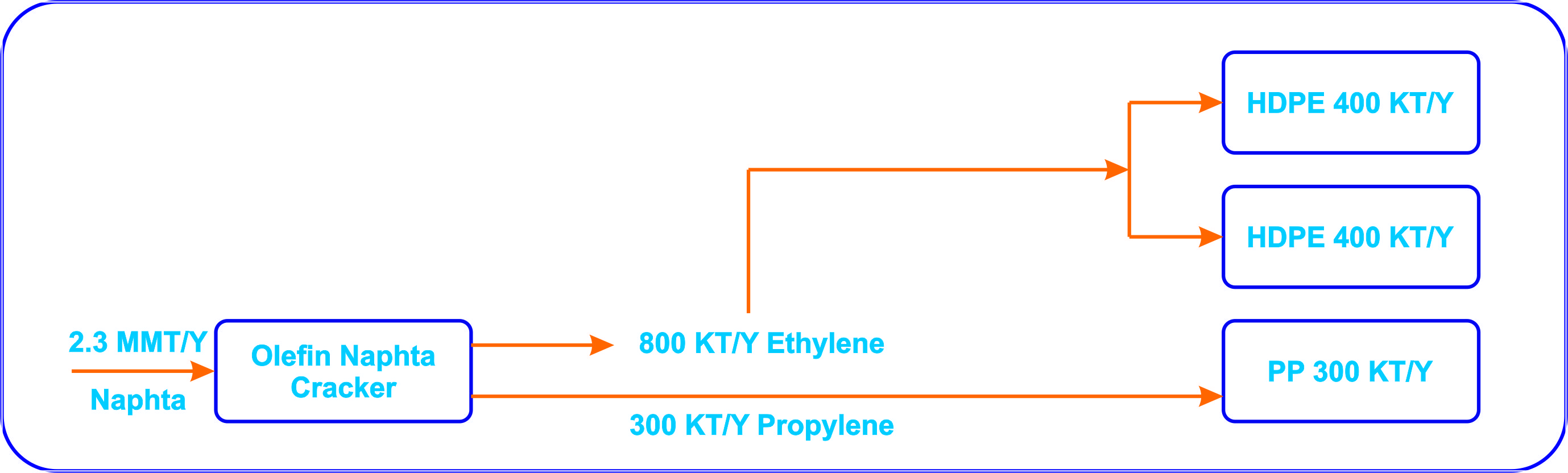
Olefin (Naphtha feed)Capacity:
800/000 MT/YearFeed:
Naphtha (1.3 MMT/Year)Product:
Ethylene 800/000 MT/Year
Propylene 300/000 MT/Year
Introduction
Light olefins such as ethylene and propylene are important building blocks for many end products like polyethylene and polypropylene. Recently market analysis shows that the demand for propylene is outgoing that of ethylene and the current supply cannot match the demand. A large proportion of propylene, about 65 wt%, is produced by steam cracking and about 30 wt% during the fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) process as a by-product.
Material Balance
Feed
2.3
172
381
43
Product
0.8
0.025
0.300
0.178
0.338
0.127
0.428